
Embark on a journey exploring the significance of genetic health screening and its impact on healthcare practices, unraveling a world of possibilities and challenges in the realm of genetic testing.
Discover how genetic health screening differs from traditional screenings and delve into the realm of identifying genetic conditions through this innovative approach.
Genetic Health Screening
Genetic health screening is a medical test that examines a person’s DNA to identify any changes or mutations that may indicate a genetic disorder or predisposition to certain conditions. This type of screening plays a crucial role in preventive healthcare by helping individuals understand their genetic risks and make informed decisions about their health.
Comparison with Traditional Health Screenings
Traditional health screenings typically focus on measuring various parameters like blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and glucose levels to assess a person’s overall health status and risk factors for common conditions such as heart disease and diabetes. In contrast, genetic health screening looks at an individual’s genetic makeup to identify inherited conditions or susceptibilities that may not be evident through traditional screenings.
Examples of Genetic Conditions Identified through Screening
- Cystic Fibrosis: A genetic disorder that affects the lungs, digestive system, and other organs.
- Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC): Caused by mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, increasing the risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
- Hemochromatosis: A condition where the body absorbs too much iron from the diet, leading to organ damage.
- Sickle Cell Anemia: An inherited blood disorder affecting the red blood cells.
Healthcare Access

Genetic health screening plays a crucial role in improving access to healthcare services by identifying individuals at risk for certain genetic conditions or diseases early on. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions and personalized treatment plans to be implemented, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
Challenges in Accessing Genetic Health Screening
- Cost barriers: Genetic testing can be expensive, making it inaccessible for individuals without adequate insurance coverage or financial means.
- Lack of awareness: Many people are unaware of the importance of genetic health screening or the availability of such services, leading to underutilization.
- Geographic limitations: Access to genetic testing facilities may be limited in rural or underserved areas, making it difficult for individuals to undergo screening.
- Cultural and language barriers: Language differences and cultural beliefs can act as barriers to accessing genetic health screening, particularly for minority populations.
Improving Access to Genetic Health Screening for Underserved Populations
- Increasing public awareness: Educating the public about the benefits of genetic health screening and the availability of services can help bridge the gap in access.
- Reducing costs: Implementing policies to make genetic testing more affordable or offering subsidies for low-income individuals can improve access to screening.
- Telemedicine and mobile clinics: Utilizing telemedicine and mobile clinics can help reach individuals in remote or underserved areas, providing easier access to genetic health screening services.
- Cultural competence training: Healthcare providers should receive training to effectively communicate with individuals from diverse cultural backgrounds and address any cultural or language barriers that may impede access to genetic testing.
Healthcare Costs
Genetic health screening can have significant cost implications for both individuals and healthcare systems. The expenses associated with genetic testing, interpretation of results, and potential follow-up care can add up quickly, making it a financial burden for many.
Cost Implications for Individuals and Healthcare Systems
Genetic health screening tests are not always covered by insurance, leading individuals to bear the full cost themselves. This can result in individuals forgoing testing due to financial constraints, potentially missing out on crucial information about their health. On the other hand, healthcare systems may face increased costs related to genetic testing, especially if a large number of individuals require screening.
Insurance Coverage and Affordability
Insurance coverage plays a crucial role in the affordability of genetic health screening. Policies vary widely in terms of what tests are covered, the extent of coverage, and out-of-pocket expenses for individuals. Lack of insurance coverage or high deductibles can deter individuals from undergoing genetic testing, impacting their access to personalized healthcare.
Strategies to Reduce Financial Burden
To reduce the financial burden of genetic health screening on patients, several strategies can be implemented. This may include advocating for insurance coverage of essential genetic tests, promoting transparency in pricing, offering financial assistance programs, and exploring alternative payment models. By making genetic testing more affordable and accessible, individuals can make informed decisions about their health without facing excessive financial strain.
Healthcare Providers
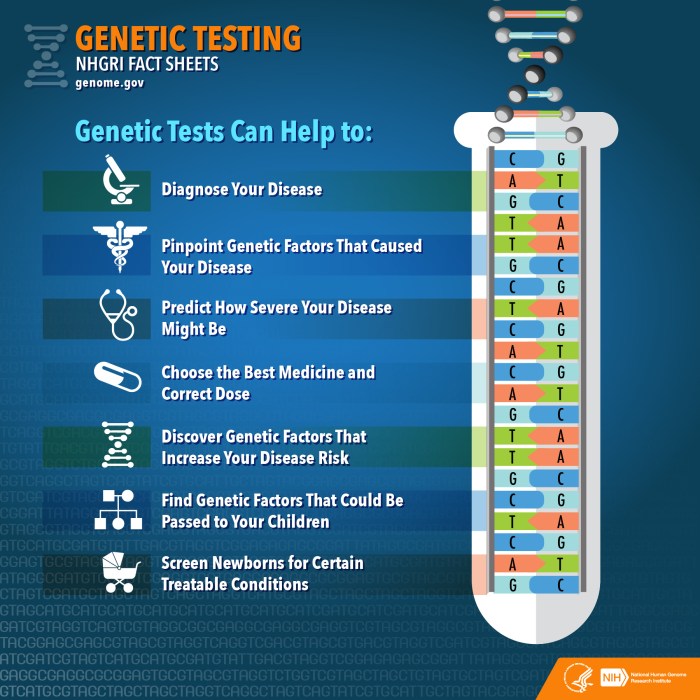
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in recommending and conducting genetic health screening for individuals.
Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, genetic counselors, and specialists, are responsible for recommending genetic health screening based on a patient’s medical history, family history, and risk factors. They also conduct the screening tests and interpret the results to provide personalized healthcare recommendations.
Importance of Genetic Counselors
- Genetic counselors are specially trained healthcare professionals who play a key role in the genetic health screening process.
- They help individuals understand the implications of genetic testing, including the risks, benefits, and limitations.
- Genetic counselors provide emotional support and guidance throughout the screening process, helping individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Training and Education
Healthcare providers involved in genetic health screening undergo specialized training and education to ensure they have the knowledge and skills to effectively recommend and conduct these screenings.
- Genetic counselors typically have a master’s degree in genetic counseling or a related field.
- Physicians and specialists may receive additional training in genetics and genetic testing to stay up-to-date with advancements in the field.
- Continuous education and professional development are essential for healthcare providers to provide high-quality genetic health screening services.
Health Insurance
Health insurance plays a crucial role in determining the accessibility and affordability of genetic health screening for individuals. It is important to understand how health insurance policies may cover or exclude genetic health screening, compare different health insurance plans in terms of genetic health screening coverage, and discuss the impact of genetic health screening on health insurance premiums.
Coverage of Genetic Health Screening
Health insurance policies vary in their coverage of genetic health screening. Some plans may cover certain genetic tests as part of preventive care, while others may require pre-authorization or consider them as elective procedures. It is essential to review the details of your health insurance plan to determine what genetic health screening services are included and any associated out-of-pocket costs.
Comparison of Health Insurance Plans
When comparing different health insurance plans, consider the coverage provided for genetic health screening. Look for plans that offer comprehensive coverage for genetic testing, counseling, and follow-up care. Be aware of any restrictions or limitations imposed by the insurance provider, such as specific testing criteria or network requirements.
Impact on Health Insurance Premiums
The impact of genetic health screening on health insurance premiums can vary depending on the insurance provider and plan. In some cases, undergoing genetic testing may result in higher premiums, especially if the results indicate a higher risk for certain health conditions. It is important to weigh the potential benefits of genetic health screening against any potential increase in insurance costs.
Health Policies
Health policies play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of genetic health screening at both national and local levels. These policies dictate the access, affordability, and ethical considerations surrounding genetic testing.
Existing Health Policies
At the national level, countries may have varying regulations regarding genetic health screening. Some nations have specific guidelines on the types of genetic tests that can be offered, who can conduct these tests, and how the results should be handled. These policies aim to ensure the quality and accuracy of genetic testing while safeguarding patient privacy and confidentiality.
Potential Policy Changes
- Introducing incentives for healthcare providers to offer genetic health screening as part of routine care.
- Implementing mandatory insurance coverage for genetic testing to make it more accessible to a wider population.
- Establishing standardized protocols for the interpretation and communication of genetic test results to patients and their healthcare providers.
Ethical Considerations
-
Ensuring informed consent: Patients must be fully informed about the benefits, risks, and limitations of genetic testing before undergoing the procedure.
-
Protecting genetic privacy: Policies should address the protection of genetic information to prevent discrimination or misuse of sensitive data.
-
Promoting equity and accessibility: Health policies should strive to make genetic health screening available to all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status or geographic location.
Health Records
Genetic health screening results play a crucial role in providing personalized healthcare decisions. Integrating these results into electronic health records can offer valuable insights for healthcare providers and patients alike.
Integration into Electronic Health Records
When genetic health screening results are integrated into electronic health records, healthcare providers have access to a comprehensive overview of a patient’s health profile. This allows for more informed decision-making and personalized treatment plans.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Storing genetic information in health records raises concerns about privacy and security. Safeguards must be in place to protect this sensitive data from unauthorized access or misuse. Strict protocols and encryption methods should be implemented to ensure the confidentiality of genetic information.
Informed Healthcare Decisions
Genetic health screening results can provide valuable insights into an individual’s genetic predispositions, allowing for proactive healthcare management. By incorporating this information into healthcare decisions, personalized treatment plans can be tailored to address specific genetic risks and improve patient outcomes.
Health Screening
Health screening plays a crucial role in preventive healthcare, allowing individuals to detect potential health issues early on. It involves various types of screenings, including genetic health screening.
Differentiate between genetic health screening and other types of health screenings
Genetic health screening focuses on analyzing an individual’s DNA for any genetic mutations or variations that may increase the risk of certain diseases. This type of screening helps identify genetic predispositions that can impact overall health. On the other hand, other types of health screenings, such as blood pressure checks or cholesterol tests, are more focused on assessing current health status or risk factors based on lifestyle and environmental factors.
Provide an overview of the process involved in genetic health screening
- Genetic counseling: Individuals may receive genetic counseling to understand the purpose, benefits, and limitations of genetic screening.
- Sample collection: A sample of saliva, blood, or tissue is collected for genetic testing.
- Laboratory analysis: The sample is analyzed in a laboratory to identify any genetic variations or mutations.
- Interpretation of results: Genetic counselors and healthcare providers interpret the results and discuss the implications with the individual.
Discuss the benefits and limitations of genetic health screening for individuals and populations
- Benefits:
- Early detection of genetic disorders or diseases.
- Personalized healthcare and treatment plans based on genetic risk factors.
- Improved understanding of family health history and inheritance patterns.
- Limitations:
- Potential psychological impact of learning about genetic predispositions.
- Accuracy and reliability of genetic tests may vary.
- Cost constraints for individuals without insurance coverage.
In conclusion, genetic health screening emerges as a pivotal aspect of healthcare, offering insights into personalized healthcare decisions and paving the way for a future where precision medicine reigns supreme.
FAQ Summary
Is genetic health screening only for specific genetic conditions?
Genetic health screening can identify a wide range of genetic conditions beyond specific ones.
Are there any risks associated with genetic health screening?
While rare, there can be risks such as false positives or negatives in genetic health screening.
Can genetic health screening results impact insurance coverage?
Yes, genetic health screening results can sometimes affect insurance coverage and premiums.





