Embark on a journey of understanding the crucial differences between HMO and PPO health insurance, unraveling the complexities of coverage, access, and costs in a clear and concise manner.
Delve deeper into the realm of healthcare options as we explore the nuances of provider networks, policy implications, and the management of health records within these two prevalent insurance types.
Health Insurance Types
When choosing between HMO and PPO health insurance plans, it is important to understand the differences in coverage and flexibility.
Difference Between HMO and PPO
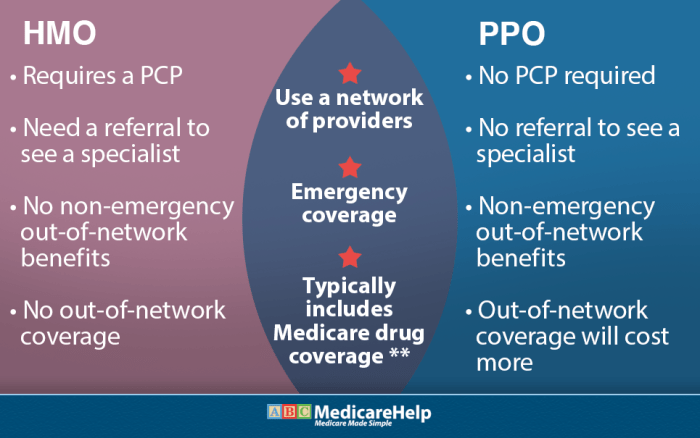
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plans typically require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and get referrals to see specialists. On the other hand, Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plans allow you to see any healthcare provider without a referral, both in-network and out-of-network.
Coverage Provided
- HMO: Offers comprehensive coverage for services within the network. Out-of-network services are generally not covered except in emergencies.
- PPO: Provides more flexibility with coverage for both in-network and out-of-network services, although out-of-network costs may be higher.
Flexibility in Choosing Healthcare Providers
With an HMO plan, you are typically required to choose a primary care physician from the network and need referrals to see specialists. In contrast, a PPO plan allows you to see any doctor or specialist without a referral, giving you more flexibility in choosing your healthcare providers.
Healthcare Access
Access to healthcare services is a critical factor to consider when choosing between an HMO and PPO health insurance plan. These two types of plans impact how you can seek medical care, obtain referrals for specialists, and navigate network restrictions.
Referrals for Specialists
In an HMO plan, you typically need to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who acts as a gatekeeper for your healthcare needs. If you require specialized care from a specialist, your PCP must provide a referral for you to see that specialist. This process can sometimes lead to delays in accessing specialized treatment but helps in managing healthcare costs and ensuring coordinated care.
- PCP acts as a central point of contact for all healthcare needs.
- Referral needed for specialist consultations or treatments.
- May lead to delays in accessing specialized care.
Network Restrictions
Both HMO and PPO plans have networks of healthcare providers, but HMOs tend to have more restrictive networks. In an HMO, you are required to seek care from healthcare providers within the plan’s network, except in emergencies. This limitation can impact your choice of healthcare providers and facilities but may result in lower out-of-pocket costs.
With an HMO plan, you must stay within the network for non-emergency care, ensuring cost-effective care but limiting provider options.
- Must use in-network providers for non-emergency care.
- Restricted choice of healthcare providers and facilities.
- Potentially lower out-of-pocket costs due to network restrictions.
Healthcare Costs
When comparing HMO and PPO health insurance plans, it’s essential to consider the cost structure associated with each type of plan. Understanding copayments, deductibles, premiums, and out-of-pocket expenses can help individuals make an informed decision when selecting the right plan for their healthcare needs.
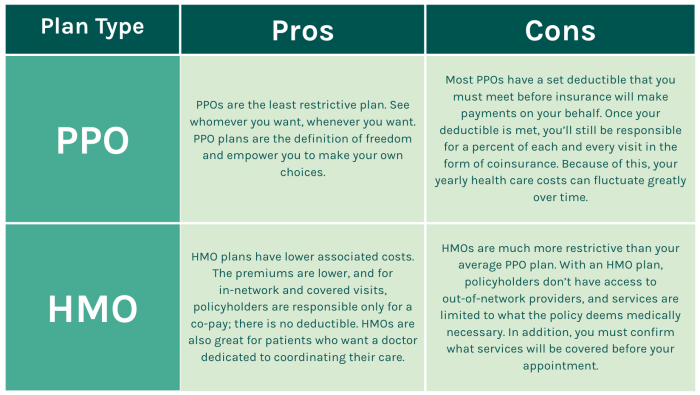
Cost Structure of HMO and PPO Plans
- HMO Plans:
- Copayments: HMO plans typically require fixed copayments for visits to healthcare providers and services.
- Deductibles: HMO plans may have lower deductibles compared to PPO plans, with some HMOs even offering zero deductibles.
- Premiums: HMO plans often have lower monthly premiums than PPO plans, making them a more cost-effective option for some individuals.
- PPO Plans:
- Copayments: PPO plans usually have higher copayments for out-of-network services compared to in-network services.
- Deductibles: PPO plans tend to have higher deductibles than HMO plans, but they offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
- Premiums: PPO plans generally have higher monthly premiums than HMO plans, reflecting the increased flexibility and choice of providers.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses in HMO and PPO Plans
- HMO Plans: In HMO plans, out-of-pocket expenses are typically lower, as individuals are required to choose a primary care physician and obtain referrals for specialist care. This structured approach helps control costs and limits out-of-pocket expenses.
- PPO Plans: PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers without requiring referrals. However, this flexibility comes at a cost, as out-of-pocket expenses, including deductibles and coinsurance, tend to be higher for services rendered outside the plan’s network.
Healthcare Providers
When comparing HMO and PPO health insurance plans, one crucial factor to consider is the network of healthcare providers available to you. Both types of plans offer different choices when it comes to accessing medical care.
Network of Healthcare Providers
In an HMO plan, you are typically required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) from a list of approved providers within the plan’s network. Your PCP will serve as your main point of contact for all medical needs and will refer you to specialists as needed. The emphasis in HMO plans is on receiving care within the network of providers to keep costs down.Conversely, PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
While you can still visit in-network providers at a lower cost, you also have the option to see out-of-network providers. However, you will pay more out of pocket for services received from providers outside of the plan’s network.The choice of healthcare provider is influenced by the type of insurance you have. In an HMO plan, you must stay within the network to receive coverage for most services.
On the other hand, PPO plans allow you to see both in-network and out-of-network providers, giving you more freedom to choose where you receive care.The importance of in-network versus out-of-network providers lies in the cost implications. Seeing an in-network provider in either HMO or PPO plans typically results in lower out-of-pocket expenses for the insured individual. Out-of-network providers may lead to higher costs, as the insurance plan may cover a smaller percentage of the bill or require meeting a higher deductible before benefits kick in.Overall, understanding the network of healthcare providers available in HMO and PPO plans is essential in making an informed decision about which type of health insurance best suits your needs.
Health Policies
When it comes to health insurance policies, both HMO and PPO plans have specific regulations that affect coverage and care options. Let’s explore how these policies differ and the impact they have on individuals seeking healthcare.
Handling of Pre-existing Conditions
- HMO Plans: HMOs typically cover pre-existing conditions, but there may be waiting periods before coverage kicks in. Some HMOs may require individuals to see a primary care physician for referrals to specialists for pre-existing conditions.
- PPO Plans: PPOs also cover pre-existing conditions, but the out-of-pocket costs may be higher compared to other services. PPOs usually do not require referrals for specialists, making it easier for individuals with pre-existing conditions to seek specialized care.
Impact of Policy Restrictions
- Policy restrictions in HMO plans often mean that individuals need to choose healthcare providers within the plan’s network. This can limit options for specialists or hospitals outside the network.
- PPO plans, on the other hand, offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, even those outside the network. However, individuals may face higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network services.
Health Records

Health records play a crucial role in ensuring proper healthcare management and treatment. Let’s explore how these records are managed and shared within HMO and PPO networks, as well as the privacy and security measures in place.
Health Records Management in HMO and PPO Networks
- HMOs typically maintain centralized health records for their members, making it easier for healthcare providers within the network to access and share information.
- PPOs, on the other hand, may have more decentralized record-keeping systems, as members have the flexibility to see out-of-network providers. This can pose challenges in sharing and coordinating health records.
Privacy and Security Measures
- Both HMOs and PPOs are required to comply with strict privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), to safeguard patient information.
- Measures like encryption, secure servers, and restricted access help protect health records from unauthorized access and ensure confidentiality.
Utilization of Electronic Health Records
- HMOs often have integrated electronic health record (EHR) systems that streamline communication among providers, leading to more coordinated care for patients.
- PPOs may rely on interoperable EHR systems that allow for data exchange between different healthcare entities, improving continuity of care but requiring stringent data security measures.
Health Screening
Regular health screenings play a crucial role in preventive care, helping to detect potential health issues early on. Let’s explore how HMO and PPO plans cover health screenings and emphasize the importance of preventive care in each type of insurance.
Health Screenings in HMO Plans
In HMO plans, coverage for health screenings is typically comprehensive and encourages preventive care. Members are often eligible for a variety of screenings at no additional cost, promoting early detection and intervention. Common health screenings included in HMO policies may consist of:
- Annual physical exams
- Blood pressure checks
- Cholesterol screenings
- Mammograms
- Pap smears
Health Screenings in PPO Plans
PPO plans also prioritize preventive care, offering coverage for health screenings to help members stay proactive about their health. While PPO plans may have more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, the frequency of covered screenings might vary. Examples of common health screenings included in PPO policies are:
- Colonoscopies
- Blood sugar tests
- Bone density screenings
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests
- Eye exams
Regular health screenings are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being, regardless of the type of insurance plan you have. By staying up-to-date with screenings recommended for your age and health status, you can take proactive steps towards preventing serious health conditions and enjoying a healthier life.
In conclusion, the decision between HMO and PPO health insurance is not just about medical coverage but also about accessibility, costs, and provider choices. By weighing these factors carefully, you can make an informed choice that best suits your healthcare needs.
Popular Questions
What is the main difference between HMO and PPO health insurance?
The main difference lies in the flexibility to choose healthcare providers and the process of obtaining referrals for specialists.
How do HMO and PPO plans affect access to healthcare services?
HMO plans usually require referrals for specialists and have stricter network restrictions compared to PPO plans that offer more flexibility in choosing providers.
Are copayments, deductibles, and premiums similar in both HMO and PPO plans?
No, the cost structure varies between the two types of insurance, with differences in out-of-pocket expenses as well.
Do HMO and PPO plans handle pre-existing conditions differently?
There may be variations in how pre-existing conditions are managed, so it’s essential to review the policies of each plan carefully.
How are health records managed in HMO and PPO networks?
Health records are typically shared and managed within the respective networks, with varying levels of privacy and security measures in place.







