Embark on a journey through the contrasting realms of urban and rural healthcare access, exploring the disparities and challenges that shape the landscape of medical services.
Delve deeper into the nuances of healthcare availability, costs, provider distribution, insurance coverage, policy influence, records management, and screening services in these diverse settings.
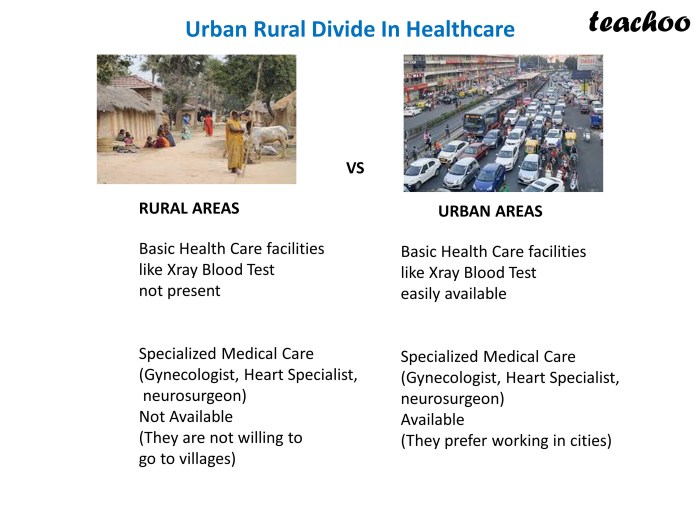
Healthcare Access Disparities
Healthcare access varies significantly between urban and rural areas, leading to disparities in healthcare outcomes and quality of care.
Differences in Healthcare Access
In urban areas, individuals have easier access to a wide range of healthcare facilities such as hospitals, clinics, and specialized medical centers. These urban settings often have higher concentrations of healthcare providers, making it more convenient for residents to seek medical attention promptly. On the other hand, rural areas typically have fewer healthcare facilities and providers, leading to longer travel times and limited options for accessing healthcare services.
Availability of Healthcare Facilities
- Urban areas have a higher density of hospitals and clinics, offering a wide range of medical services and specialties.
- Rural areas often lack hospitals and specialized medical facilities, forcing residents to travel long distances for essential healthcare services.
- Telehealth services are more prevalent in urban areas, providing convenient access to medical consultations remotely.
Impact of Geographical Location
The geographical location plays a significant role in determining healthcare access. Urban areas benefit from better infrastructure, transportation networks, and healthcare resources, resulting in improved healthcare access and outcomes. Conversely, rural areas face challenges such as provider shortages, limited healthcare infrastructure, and geographical barriers, leading to disparities in healthcare access and health outcomes between urban and rural populations.
Healthcare Costs Disparities
Healthcare costs can significantly vary between urban and rural areas, impacting the accessibility and affordability of medical services for residents.
Cost Variations Based on Location
One key example of cost disparities is seen in the price of prescription medications. In urban areas, where there is higher competition among pharmacies and healthcare facilities, prices for medications tend to be lower compared to rural areas where access to pharmacies may be limited, leading to higher costs for the same medications.
Additionally, the cost of medical procedures and treatments can also differ based on location. For instance, elective surgeries or specialized treatments may only be available in urban hospitals, leading rural residents to incur additional expenses for travel and accommodations in order to access these services.
Factors Contributing to Cost Variations
- Population density: Urban areas with higher population density tend to have more healthcare providers and facilities, leading to increased competition and lower prices.
- Infrastructure: Rural areas may lack the infrastructure needed to support a wide range of healthcare services, resulting in higher costs for residents who must travel to urban centers for specialized care.
- Health insurance coverage: Differences in health insurance coverage rates between urban and rural populations can also impact the out-of-pocket costs for medical services.
- Economic disparities: Income levels in rural areas may be lower on average, making it more challenging for residents to afford healthcare services, even if the actual cost is lower than in urban areas.
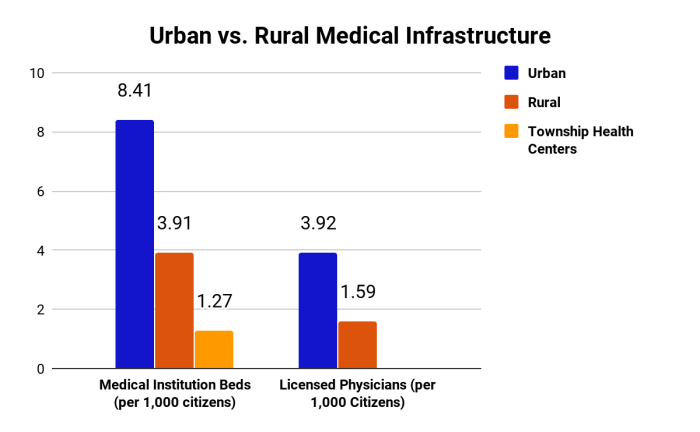
Healthcare Providers Distribution
In urban areas, the distribution of healthcare providers is generally more concentrated due to a higher population density and greater demand for services. On the other hand, rural areas often struggle to attract and retain healthcare professionals, leading to disparities in access to care.
Challenges in Rural Areas
- Rural areas often face challenges in attracting healthcare professionals due to lower salaries, limited career advancement opportunities, and a lack of amenities compared to urban areas.
- The remote location of many rural communities can make it difficult for healthcare providers to access necessary resources and support, leading to feelings of isolation and burnout.
- Limited educational and training opportunities in rural areas can also hinder the recruitment and retention of healthcare professionals, as individuals may need to relocate for higher education or specialized training.
Impact of Provider Shortages
- The shortage of healthcare providers in rural regions can result in longer wait times for appointments, reduced availability of specialized services, and limited access to preventive care.
- Patient outcomes may be negatively affected by the lack of healthcare providers in rural areas, as individuals may delay seeking care or have to travel long distances to receive necessary treatment.
- Healthcare disparities between urban and rural areas can widen due to the unequal distribution of providers, leading to poorer health outcomes and increased healthcare costs for rural residents.
Health Insurance Disparities
In the realm of healthcare access, disparities in health insurance coverage between urban and rural populations play a crucial role in shaping the quality and availability of healthcare services.
Impact of Insurance Availability on Healthcare Access
- Individuals in urban areas tend to have higher rates of health insurance coverage compared to those in rural areas. This discrepancy can significantly affect the ability of individuals in rural areas to access timely and affordable healthcare services.
- Health insurance coverage not only influences the type of healthcare services individuals can access but also impacts their financial burden when seeking medical care. Lack of insurance in rural areas may lead to delayed treatment or avoidance of necessary medical services due to cost concerns.
- Insurance availability influences the choice of healthcare providers and facilities that individuals can access. In rural areas with limited insurance options, individuals may face challenges in finding healthcare providers who accept their insurance, further exacerbating disparities in healthcare access.
Role of Health Insurance in Mitigating Healthcare Access Disparities
- Health insurance plays a vital role in mitigating healthcare access disparities by providing individuals with financial protection and access to a network of healthcare providers. In urban areas where insurance coverage is more prevalent, individuals are more likely to seek timely medical care and preventive services, ultimately improving health outcomes.
- By expanding health insurance coverage in rural areas, policymakers can help bridge the gap in healthcare access disparities between urban and rural populations. Increased access to insurance can enhance the affordability of healthcare services and reduce barriers to seeking necessary medical care in underserved rural communities.
- Efforts to improve health insurance availability and affordability in rural areas can lead to better health outcomes, reduced disparities in healthcare access, and overall improvements in population health. Addressing health insurance disparities is essential in creating a more equitable healthcare system that meets the needs of all individuals, regardless of their geographic location.
Health Policies Influence

Health policies play a crucial role in shaping healthcare access in both urban and rural areas, influencing factors such as funding allocation, service delivery, and overall healthcare infrastructure.
Implementation Disparities
When it comes to implementing healthcare policies, urban areas often have better access to resources and infrastructure compared to rural settings. This can lead to disparities in the quality and availability of healthcare services between the two areas.
Effectiveness of Current Policies
- Current policies may not adequately address the unique needs of rural populations, leading to continued disparities in healthcare access.
- Efforts to bridge the gap between urban and rural healthcare access through policy interventions are essential to ensure equitable healthcare for all individuals, regardless of their geographic location.
- Regular evaluation and adaptation of healthcare policies are crucial to address evolving healthcare access disparities and ensure effective implementation.
Health Records Management
Maintaining health records is a crucial aspect of healthcare delivery, ensuring accurate and efficient treatment for patients. However, there are significant challenges in managing health records in both urban and rural healthcare settings.
Challenges in Health Records Management
- In urban areas, the high volume of patients and complex healthcare systems can lead to difficulties in organizing and updating health records in a timely manner.
- On the other hand, rural areas often face issues with limited access to technology and internet connectivity, making it challenging to maintain digital health records.
- Additionally, healthcare facilities in rural areas may lack standardized systems for health record management, leading to discrepancies and errors in patient information.
Impact of Digital Health Records
- Digital health records have revolutionized healthcare access by enabling seamless sharing of patient information among healthcare providers, resulting in improved coordination of care.
- Patients in both urban and rural areas can benefit from digital health records, as they reduce the risk of duplication of tests, medication errors, and ensure continuity of care.
- However, the implementation of digital health records requires significant investment in technology infrastructure and training, which may be a challenge for healthcare facilities in rural areas with limited resources.
Differences in Health Record Systems
- Urban healthcare facilities often have sophisticated electronic health record systems that allow for real-time updates, data analysis, and decision support tools to enhance quality of care.
- In contrast, rural healthcare facilities may rely more on paper-based records or basic electronic systems due to budget constraints and lack of technical expertise.
- This disparity in health record systems can impact healthcare access and quality of care, as rural facilities may struggle with data integration and interoperability issues when collaborating with urban providers.
Health Screening Disparities
Health screenings play a crucial role in preventive healthcare by detecting potential health issues early on. Disparities in health screening services between urban and rural areas can have a significant impact on individuals’ access to these important preventive measures.
Availability of Health Screening Services
In urban areas, access to a variety of health screening services is typically more readily available. Hospitals, clinics, and specialized healthcare centers often offer a range of screening tests for conditions such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. On the other hand, rural areas may have limited healthcare facilities, leading to a lack of access to comprehensive health screenings.
Barriers to Access
Individuals in rural areas face several barriers when trying to access health screening services. Factors such as geographic distance, transportation limitations, and healthcare provider shortages can all contribute to the difficulty in obtaining regular screenings. Limited financial resources and health insurance coverage may also hinder individuals from seeking out necessary health screenings.
Importance of Health Screenings
Regular health screenings are essential for early disease detection and prevention. By identifying health issues at an early stage, individuals can receive timely treatment and interventions, leading to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs in the long run. Health screenings also help in promoting a healthier lifestyle and raising awareness about various health conditions within the community.
As we conclude our exploration, it becomes evident that addressing the discrepancies in healthcare access between urban and rural areas is crucial for ensuring equitable and quality healthcare for all individuals, regardless of their geographical location.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the main differences in healthcare access between urban and rural areas?
Urban areas typically have better access to healthcare facilities and services compared to rural areas due to higher population density and infrastructure.
How do healthcare costs vary between urban and rural areas?
Healthcare costs tend to be higher in urban areas due to increased demand, competition, and operational expenses, whereas rural areas may face affordability challenges.
What challenges do rural areas encounter in attracting and retaining healthcare professionals?
Rural areas often struggle with limited resources, isolation, and lower income potential for healthcare professionals, making it challenging to retain and recruit skilled providers.
How does health insurance coverage differ between urban and rural populations?
Urban populations generally have higher rates of health insurance coverage compared to rural populations, leading to disparities in access to healthcare services and treatments.
What role do health policies play in influencing healthcare access in urban and rural areas?
Health policies can shape the availability, quality, and affordability of healthcare services, impacting access and health outcomes differently in urban and rural settings.





